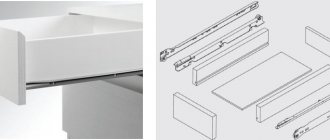
When assembling furniture, you often have to deal with the choice of guides with the help of which drawers are pulled out. They can be of different sizes, colors or types, but the main feature is that they can easily allow the drawer to be pulled out and pushed in. The service life of the entire structure and ease of use throughout its entire service life depend on the quality of components and installation. In this article we will look at what types of drawer guides exist and what their differences are.
How to calculate drawers for telescopic guides
Initially, for the manufacture of boxes and drawers, 16mm thick chipboard will be used, and telescopic guides will be used for retractable fittings.
So, first, let's figure out how to calculate the sizes of the boxes.
Any such piece of furniture consists of four parts.
As a rule, two front parts are located between two side parts (to which the runners from the telescopic guides are then attached).
In order to calculate the dimensions of the front parts, we need to know the width of the entire box.
Let it be equal to S.
For calculations, we also need to know the clearances that need to be given on the telescopic guides. They are equal to 13mm (for each guide).
Sfr = S-32-26-32 = S-90 (mm, all dimensions in the future will be in millimeters), where: 32 is the thickness of the two sides of the box, 26 is the tolerances for the guides on both sides (13+13=26 ), 32 – the thickness of the two side parts of the box.
The formula Sfr = S-90 can be used if, as mentioned above, the chipboard thickness is 16 mm.
If, for example, the chipboard thickness is 18mm, then:
Sfr = S-36-26-36 = S-98
The side parts of the drawer are usually equal to the dimensions of the guides themselves, which are:
The most common option (for example, for the manufacture of kitchen sets - a box, 460 mm deep, for guides, 450 mm in size).
For example, in our version, the upper facade will have a standard height of 140mm, and the height under it can be 100mm.
But for the other two facades, each 291mm high, this height can be taken, for example, 120, 150, 180.... In our case, it will be equal to 200mm.
Now, a rather important moment is marking the sides of the box for installing “telescopes”.
The markings must be correct, since the drawers must be located inside the box at a certain distance from each other. All this is “tied” to the position of the facades and the gaps between them.
So how do you make this markup?
First, you need to decide on the position of the facade relative to the drawer.
In the case of the upper facade, it will be located strictly along the central axis of the drawer.
The remaining two facades will be positioned so that the distance between the drawer parts and the bottom edge of the facade is equal to, for example, 25mm.
The fact is that the lowest facade will overlap the box (at the bottom) flush.
Since the lower horizon of the box is 16mm thick, there must still be a gap between this horizon and the drawer (so that the latter can move without catching this horizon).
25-16=9 (mm). This will be the size of the gaps.
Even if in this calculation we include the thickness of the fiberboard (from which the bottom of the box will be made), the thickness of which, for example, will be equal to 3 mm, then:
As you can see, there is a gap, everything will work.
And the last condition: For simplicity of calculations, that part of the telescopic guide that will be attached to the drawer will be attached strictly in its center.
Facade sizes: 140mm and 291mm.
The upper gap between the facade and the frame is 4 mm, and the gaps between the facades are 2 mm.
We mark the side from the top down.
But in order to start making markings, you need to determine the position of the guide axis on the drawer with the front.
In the case of the upper facade, it will be equal to 70mm above and below.
In the case of the other two fronts, it is calculated as follows:
Since the gap between the front and the drawer (bottom) is 25mm, and half the height of the drawer itself (200mm) is 100mm, the distance from the bottom of the front to the central axis of the drawer will be equal to:
Then the distance from the top edge of the facade to this central axis will be equal to:
291-125=166 (mm), where 291 is the height of the facade.
So, we calculate the position of the upper guide (all dimensions will be in millimeters):
4+70=74, where 4 is the gap between the upper facade and the upper edge of the box.
74+70+2+166=312. This is the position of the axis under the second drawer.
312+125+2+166=605 – position of the axis under the third (lower) drawer.
Source
Advantages of MB guides in comparison with DS guides
- The greater thickness of the metal in combination with a higher counter part allows you to increase the payload of the furniture box.
- The reinforced counter part of the MB guides allows the use of more massive facades from various materials for the production of furniture boxes, which makes it possible to create boxes with different front designs.
- The sufficient height of the counter part of the MB guides makes it possible to install an eccentric mechanism for adjusting the facade on it, which allows you to adjust the position of the facade in height in the range of ±2 mm.
Lesson 19 — How to calculate the dimensions of facades in cabinet furniture
Calculation of facades is a fairly important procedure, because they are the face of the finished product and in some cases (for example, MDF facades) it will not be possible to change anything if there is an error.
In this article I will try to explain how calculations are made for all the main types of furniture facades (with the exception of sliding doors and radius doors). We will disassemble it on the basis of a box with external dimensions of 600 x 300 mm.
So, let's start with swing facades. In order for the doors to open, it is necessary that they do not rub against each other and against the body; technological gaps are provided for this.
They are 2-4 mm (more - they look ugly, less - they rub).
Personally, I prefer to make gaps of 2 mm.
Separately, I note that the dimensions must be calculated for each module separately, that is, if you are assembling a kitchen in which there are 3 floor drawers and 3 wall drawers, then the dimensions must be calculated for each drawer separately, that is, 6 times - this way you will insure yourself against a number of possible mistakes.
The width of the facade is calculated using the formula:
w = (W/n)-3 mm
where w is the width of the facade, W is the width of the box, n is the number of facades (by width)
Some furniture makers subtract 4 mm, but in my opinion the gaps are too large.
Height of facades. When calculating height, there are no clearly defined formulas - you should be guided by common sense and some simple subtleties.
For example, let's calculate the dimensions of the facades for several kitchen modules.
in red , the gaps in blue in orange .
So, the dimensions of the box are 730×450 mm
We calculate the width using the formula (450/1)-3 and get 447 mm. (there are 1.5 mm gaps on the sides, which will allow you not to cling to adjacent cabinets, which will have the same allowances).
In terms of height, we decide to make 3 facades, of which 2 are large, 300 mm each. We take into account that the optimal distance between adjacent drawers is 2-3 mm , and between the tabletop and the upper facade 5 mm (so that the facade does not cling to the drip tray, which is found on kitchen countertops). As a result, subtracting these values from the height of the box, we obtain the height of the small facade 121 mm
730mm - 300mm - 2mm - 300mm - 2mm - 5mm=121 mm
Let's move on to another example: calculation of facades for a hanging cabinet. Its peculiarity is the presence of two hinged facades, as well as an overhang of the upper horizon, which seems to cover the doors, giving the entire cabinet a finished look.
Based on the overall dimensions of the cabinet: 636 x 600 mm, we calculate the width of the facades. (600/2)-3 = 297.
Knowing that the thickness of the upper horizon is 16 mm, and making a 3 mm gap between it and the facade, we get the height of the facade (636-16-3) = 617
Now let's move on to the individual subtleties of the calculation.
1. When calculating the dimensions of facades made of laminated chipboard edged with 2 mm PVC edges, do not forget to subtract another 4 mm from the dimensions, both in height and width (edge thickness on both sides)
2. When calculating the dimensions of hinged facades
for corner cabinets, it is necessary to take into account that there are two types of corner hinges (+45, +30 g).
Visually they do not differ from each other; the difference is noticeable only on the assembled body with a hung facade. Therefore, the installation diagram for the corner hinges that you purchase should be checked with the seller. Let us analyze the calculation for each using the example of a corner cabinet with a distance between the walls (in the façade opening) of 300 mm.
So, option 1, the facade turns out to be inset; its size should be 1 mm less than the width of the niche, that is, equal to 299 mm.
Option 2, on the contrary, provides for the overhead nature of the facade. In this case, the facade is 5 mm wider than the niche (305 mm)
Let us separately dwell on such a topic as the calculation of sliding doors in various variations
Calculation of sliding facades of the "Versailles" straight cabinet system
Calculation of facades-compartments “Versailles” corner wardrobe
How to avoid calculation errors
Any type of furniture begins to be calculated by determining its dimensions. In the case of a kitchen set, this is also true, but you first need to estimate the size of the room and start from its shape, corners and other important details. Then all the numbers found are transferred to paper and a design sketch begins to be developed.
Please note that the dimensions of the bottom base must be related to the length of the tabletop. The size of the fronts of the corner cabinets depends on the characteristics of the room. For example, in the case of high ceilings, horizontal gaps may be larger than standard.
Bottom part
To determine the width of the bottom row of furniture, the gaps from all edges are subtracted from the total value. After this, the resulting value is distributed among the planned headset modules. To calculate the height, it is important to remember the size of the niches for household appliances. The standard is 850 mm.
Upper cabinets
When designing the upper module, it is necessary to take into account that the hood should be located strictly above the stove, and the dryer - above the sink. Standard furniture allows for changing the layout; cabinets can be rearranged for ease of use.
Standard or non-standard?
So, if you are at the planning stage of your future kitchen, then, most likely, you already know that you will have to buy ready-made fronts from some manufacturer that will offer you products of non-standard and standard dimensions. Before we begin calculations and design, let's figure out what the difference between these categories is.
Conclusion: it turns out that it is more profitable and easier to draw up a project, adapting as much as possible to the standard dimensions of the fronts, but if necessary, order the production of products of non-standard width/height.
The table below shows the standard sizes of blind doors, display cases and drawer fronts.
Standard dimensions of kitchen facades
Paint quality (including color consistency) for DS and MB guides
High-quality painting is achieved by following the following technology:
- Preliminary preparation of the surface before painting: mandatory degreasing, removing the oil film and the natural oxidized layer of the metal
- Painting: only the use of professional enamel and automated painting equipment can provide a high-quality, uniform and uniform layer of paint on the product, including uniform painting of all recesses without smudges.
- Drying in a special chamber at a certain temperature for a strictly controlled time.
- DS guides are available in white (W), brown (Br), black (Bl) and gray (GR).
- MB guides are produced in white (W) and gray (GR) colors.
A little “furniture” mathematics - we do the calculations correctly
Now let's start calculating the overall dimensions of the facades.
The general principle of calculation is simple: the width/height of the facade must be less than the width/height of the body, therefore, the technological gap must be subtracted from any width/height of the body:
The gap can be 1-2 mm on each side, respectively 2-4 mm - the overall gap size.
It would seem that everything is simple, but still there are some nuances for some modules.
Keep in mind that for each module (especially for MDF fronts, since they cannot be adjusted) it is better to do separate calculations - this way you will avoid irreparable errors.
Now let's look at these nuances using the example of a 700x400 mm module, with a total gap of 3 mm.
Nuance 1. How to calculate the width of the facade for a building with two hinged doors?
In this case, an additional 3 mm must be subtracted from the width of the cabinet for the gap between the two hinged doors. You will get the following calculation for one door:
Nuance 2. How to calculate the width of the facade for a building adjacent to the wall?
If the cabinet is adjacent to a wall, then from the width of the cabinet you need to subtract 3 mm (for the gap at the wall) and 1.5 mm for the gap with the facade with the adjacent door. We count like this: 400–3 mm-1.5 mm = 395.5 mm.
Nuance 3. How to calculate the size of the facade for the lower body located under the countertop?
If the countertop has a drip tray, then the gap between it and the upper edge of the facade should be 4-5 mm. If a drip tray is not provided, then the gap can be made 3 mm.
Nuance 4. How to calculate the height of the facade located under/above the decorative cornice?
Here we subtract 3 mm from the height of the body for the connection to the upper cornice. If there is also a lower cornice, then subtract another 3 mm (6 mm in total).
Nuance 5. How to calculate the dimensions of the fronts for drawers?
If there are several identical drawers in one case, then the height of the linings can be calculated using the following formula:
If the body with drawers is located on the floor with a tabletop, then we take into account the additional gap in the calculation:
Let's give an example: if the height of the case is 860 mm, it has 4 drawers, and the case is located under the countertop, then we get the following calculation:
If it is assumed that the drawers have different heights, then the calculation must take into account the height of each drawer, the number of drawers in the body and the gap.
To calculate the width of box fronts, the same principles are used as for doors.
Source
How to reduce gaps on facades
Some buyers want to get the effect of monolithic furniture, when the fronts fit closely together and the gaps are almost invisible. The task becomes more complicated if the edges of the facades are required to be straight, without changing the shape. In this case, it is necessary to carefully select the material for the headset. For example, MDF products are definitely not suitable here, and some sizes of PVC panels will look rounded. To solve this problem, you can purchase material with a thickness of 0.4 mm. This size will allow you to slightly reduce the facades, but at the same time maintain the desired appearance of the furniture.
It should be borne in mind that with such large gaps, minimal door play is necessary, otherwise there is a risk of catching adjacent cabinets. This is especially difficult to implement in the lower sections if there are storage drawers there. When installing furniture, all elements are adjusted empty, but they sag much more under the load of things. With a backlash of only 1 mm, even a slight load can lead to jamming of the drawers, which will negatively affect their operation. Therefore, it is recommended to think carefully before making such a decision.
Roller or ball guides, which one to choose?
From the point of view of calculating drawers, the formulas for roller and ball guides are absolutely the same. You can change one on a chest of drawers, a cabinet or a closet at any time without any changes in the design of the furniture. The only caveat is that there will be holes left from the fasteners, which can be masked somehow, because:
If we talk about which of the above guides is better, then the answer lies in the budget allocated for the manufacture of cabinet furniture.
Roller guides are economical. They are used on production office furniture. As in principle, ordinary roller guides are installed on any drawers of economy-class cabinet furniture, including kitchen ones. Fittings of this type are quite practical and durable. If you don’t heavily load the box (and the bottom made of thin fiberboard won’t allow you to do this), then it will last for decades. The design of the roller guides is such that there is nothing to break there.
Full extension ball guides are in a higher class in terms of cost and performance characteristics. A drawer equipped with them extends completely, without blocking the back part with the top shelf (table top), which is very convenient for viewing everything stored in it. Also, ball guides boast a smooth, pleasant motion. There are options with a built-in closer (they can be identified by a spring built inside the mechanism with a plastic stop).
When choosing retractable mechanisms, you should not chase cheapness. A lot depends on the thickness of the metal and the accuracy of the calibration. Chinese analogues with thin metal fail very quickly - the guides themselves wrinkle and bend, rollers and ball bearings fly out even under non-critical loads. Therefore, be careful when purchasing and give preference to high-quality, popular items from well-known budget brands.
Design and material of guide roller DS and MB
The presence of rubber-coated rollers, which ensure quiet running, is a false impression of the quality of the DS and MB guides.
There are two types of rubberized rollers: composite and solid.
- Composite ones
consist of two parts with a rubber gasket. - Solid
- with a longitudinal groove in which a rubber roller is located.
Previously, by using a rubber softening pad, the noise of the guides was reduced, but the use of rubber led to increased friction between the roller and the guide, as a result of which opening and closing the drawer was difficult and inconvenient. Such roller designs significantly reduced its wear resistance, consumer and operational properties of products, and the roller was destroyed. Modern DS and MB guides of high quality from well-known manufacturers use rollers made of POM polymer (polyoxymethylene), as well as rollers made of ABS plastic material.
- POM
(polyoxymethylene, polyformaldehyde, polyacetal) (—H2C—O—)n is a polymerization product of formaldehyde. It is characterized by high stability, maintains rigidity and mechanical strength up to 120°C, is resistant to abrasion, shock loads, organic solvents and oils. It is a self-lubricating material, resistant to low temperatures, which is important during transportation and storage in warehouses. - ABS plastic
is an impact-resistant technical thermoplastic resin based on a copolymer of acrylonitrile with butadiene and styrene (the name of the plastic is formed from the initial letters of the names of the monomers). It is characterized by high hardness and strength, resistance to impact loads.
Calculation of drawers
To avoid confusion and misunderstanding, let’s define the initial data:
The furniture is made of laminated chipboard with a thickness of 16 mm; fibreboard with a thickness of 4 mm is used for the bottom.
Calculation of the drawer front
Whatever one may say, the calculation of the inside of the box largely depends on the front part.
The facade can be internal (rolled over the side walls of the body) or overhead.
As you can see from the drawing, the choice of overlay or internal front can affect the depth of the drawer. In the case of an inset one, it is rolled deeper to the thickness of the facade (-20 mm from the depth of the stand).
The height of the drawer front usually varies between 150-200 mm. It all depends on what will be stored inside. For documents and stationery in office cabinets, smaller drawers are made, 120-150 mm deep, rarely 180 mm. The linen drawers of the chest of drawers are designed deeper, ranging from 180 mm to 250 mm. For toys and bedding, drawers can be even deeper along the height of the facade, but in this case it is necessary to reinforce the bottom with a stiffener or partitions.
The size of the drawer fronts, taking into account the technological gap, is calculated by analogy with other doors; you can read more in detail here. In short, 2-3 mm is subtracted from the dimensions along the outer perimeter; the gap between adjacent facades is also 2-3 mm.
An example of how to calculate the fronts for two drawers relative to our cabinet with dimensions X*Y*Z.
The height and length of the facade can be swapped if there is a texture and the desired direction of the pattern - longitudinal or transverse. When edging PVC facades around the perimeter, it is necessary to take into account the thickness of the edge!
How to calculate the side of a box
Drawer guides are available in 50 pitches, ranging from 250 mm to 550/600 mm. Hardware manufacturers always have a similar layout in their catalogs, which can help you navigate the dimensions and markings for fasteners.
roller guide dimensions
ball guide dimensions
Thus, the depth of the sides of the drawers is taken in increments of 50. For the shallowest drawers, 250 mm, and further, correlating the depth of the standing cabinet/cabinet with the length of the suitable guide - 300, 350, 400 mm, etc.
The narrowest side of the cabinet/cabinet for built-in is 260 mm for the overlay facade and 280 mm for the internal facade (for a 250 mm guide). The required clearance at the front edge for installation is usually 2 mm. The gap at the back is arbitrary, from 1-2 cm to 5 cm. If there is more left, it is better to purchase longer guides so as not to waste space behind the drawer. It turns out:
(drawer depth) = length of the guide and less than Z by no more than 50 mm.
How to calculate the front (front and back) of a drawer
If we again turn to the manufacturers' catalogs, we can see that the gap between the sides of the cabinet/cabinet body and drawers is about 12.5-12.7 mm.
In fact, when calculating, these numbers are rounded by subtracting 13 mm. This makes the drawer move more freely and is easier to adjust.
In the drawing, the calculation diagram for the box is clear and understandable. Thus, to calculate the “forehead” of a drawer, you need to subtract the thickness of the chipboard from the dimensions of the cabinet/cabinet 4 times (2 on each side) and a gap of 13 mm, also on both sides. 16*4+13*2=90. It turns out:
(forehead length)=X-90mm.
How to calculate the depth of a drawer
There are no special standards regarding depth. Usually 10-20 mm are left under the facade (Z5), and 30-80 mm above the facade.
Thus, if, for example, the height of the facade is 150 mm, then the depth of the drawer will be about 80-100 mm. I base my calculations on the cut cards. If reducing the depth of the drawers allows you to more compactly place the parts on a sheet of chipboard, then this is worth taking advantage of. There are situations when several parts fit onto a new sheet, but if you “play” with such unprincipled dimensions of the parts, you can save on buying a whole sheet with a huge remainder!
Fiberboard bottom calculation
There are two ways to install the fiberboard bottom - overlapping and in a groove. In the first case, the bottom is nailed to the drawer frame from the back side. In the second, it slides into a special groove.
Calculation of a drawer using an example
How to calculate the dimensions of parts for drawers in a niche 400 mm wide, 500 mm deep and 600 mm high. Let there be internal facades, the gap is not 3, but 4 mm for each (2 mm on each side), taking into account an edge 0.5 mm thick. The bottom is attached with an overlap.
It is most convenient to enter formulas in Excel tabular form, indicating the names of the parts and their size (length and width), quantity.
Source
How to calculate the dimensions of cabinet doors and drawers
The front part requires utmost attention - after all, it is the quality and finishing of the doors that determines the design and “status” of the furniture. It is important not only to choose beautiful facades, but also to correctly calculate the dimensions of the cabinet doors, with uniform gaps for trouble-free opening. Errors in calculations are unacceptable, because most often it will not be possible to redo the facade, you will have to order it again. This means time and additional costs.
You can read how to calculate the fronts for a wardrobe here. This article will describe the process of calculating the sizes of swing doors and drawers for cabinet furniture (including kitchens).
Corner sets
Such kitchens require a special approach when installing and choosing furniture. There is a wide variety of sizes of corner facades and cabinets, but they need to be chosen in such a way that they coincide with straight ones in terms of the main parameters.
Characteristics of mounted models:
Main properties of floor cabinets:
A special feature of the lower row of the headset is its installation, which is carried out after the installation of the upper elements. At the same time, you need to ensure that the placement is symmetrical so that the floor products do not go beyond the wall-mounted ones.
Minimum and maximum cabinet door size
For a swing facade, the dimensions are strictly limited by the ability of the furniture hinges to support its weight. If the load is disproportionate, the cabinet doors will inevitably sag and adjusting the hinges will only give a temporary effect. The weight of the facades is capable of tearing fasteners out of the side walls. Therefore, at the design stage it is necessary to correlate the desired dimensions of the facades with the possible ones, according to the technical characteristics of furniture hinges.
Usually, when determining the number of hinges and the size of the cabinet doors, they rely on the following table:
The maximum permissible width of the facade is about 500-600 mm. For large sizes, it is worth considering the option with two swing doors or sliding systems.
The maximum permissible height (length) of the facade is about 2200 mm. If you make the door longer, it will be inconvenient to open it.
The minimum dimensions are limited only by considerations of aesthetics and functionality. If the cabinet body is narrower than 300 mm, the hinge mounting pads should be screwed in before assembling the body itself.
The principle of calculating the dimensions of swing doors and drawer fronts
According to the generally accepted standard, the gap between the sashes should be about 1.5-2 mm. To calculate the size of the front for the drawer, the same gaps are used. And not only so that it “looks” the same with the doors. But also because the loaded box sags a little, and the gap serves as a kind of “insurance” that the facades will not rustle against each other when they are pulled out.
For kitchen furniture, it is customary to subtract 4 mm from the dimensions of the niche. For example:
But many people find that a gap of 4 mm is too much. Therefore, leave 3 mm, as for all other cabinet furniture. This is completely acceptable and not an error.
Nuance! When subtracting 3 mm for gaps, do not forget that you are calculating the final dimensions for the cabinet doors. If these are facades made of laminated chipboard and will then be edged with 2 mm thick PVC, then this should be taken into account. And subtract not 3 mm, but 7 (+2 mm will be added on each side, total 3+2+2). The same applies to façade options with aluminum ends and other types of edges.
To calculate the dimensions of drawer fronts, the same principle is used: subtract 1.5 mm from each side.
For example, in a cabinet 720x400 it is planned to install three drawers, two narrow and one wide. We divide the cabinet according to the height with the desired capacity of the drawers, let it be 180+180+360, as for kitchen furniture. We get the dimensions of the facades:
If you decide to leave a 3 mm gap on all furniture:
If the facades are designed for a 2 mm thick PVC edge:
For the internal facades of the cabinet, the calculations will be similar. You should only subtract 3-4 mm from the internal dimensions of the niche.
How to calculate the dimensions of corner cabinet doors
The main difficulty in calculating doors for a corner cabinet is determining the width of the sash. To do this, first calculate the width of the opening. Here you will have to remember school mathematics and the well-known formula - the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the length of the legs.
Let's take as an example a wall-mounted corner kitchen cabinet, standard dimensions 600x600 and side depth 300 mm.
With a sidewall thickness of 16 mm, the length of the legs will be (600-300-16) = 284 mm.
We calculate the opening in two steps: 284x284x2 = 161312, without the square root of 401.63. Round up to 401.
When calculating the width of the façade for a corner cabinet, one nuance is taken into account: due to the furniture hinge, the door will “move forward” a little and will not fit tightly into the opening. That is, it will come out on a large diagonal and the gaps will form on their own. Therefore, it is not worth subtracting 3 mm from the opening size, as for ordinary cabinets. In our case, we can round up to 400 mm.
But the height is calculated similarly to conventional cabinets. In our case, for a kitchen module with a height of 720 mm, it will be 717-716 mm (depending on how the rest of the kitchen facades were calculated, with a gap of 4 mm or 3 mm).
If the opening width is more than 500 mm, then there is a reason to install not one, but two sashes. When calculating the width, it is necessary to take into account the gap between the facades so that the doors do not interfere with opening to each other. That is, with an opening width of 600 mm for a corner cabinet, the width of each door should be about 298 mm.
Important nuance! This calculation method is only valid for facades whose thickness is comparable to the thickness of the cabinet body sides. For example, the body is 16 mm laminated chipboard, the facade is 16-18 mm thick laminated chipboard or MDF. If the facades are much more massive, 20-22 mm thick, then a gap is simply necessary to open them and it can be significant, up to 10 mm.
How to increase the distance between fronts
In some design ideas, the opposite situation is present - it is necessary to install a set with large and pronounced gaps between the facades, which emphasize the style of the room. This solution really looks very unusual and creates a bright accent in the interior. In this case, you will have to not only calculate the distances, but also adapt the furniture frame so that gaps do not appear in the spaces.
When reducing the size of doors relative to the body, there are some things to consider. For hinged facades, they do not purchase standard hinges, but special semi-overlay hinges, which allow you to open the cabinet at half the end. The doors should also be reduced by this amount, which is usually between 8 and 10 mm.
As for the drawers, the increased gaps here do not make any difference from a practical point of view.
Dimensions of beveled end cabinet doors
Often a row of kitchen or wardrobe cabinets ends with an end module with a beveled door. Its width is calculated by analogy with the previous option with the only difference.
Initially, you also need to calculate the width of the opening. Here you need to be prepared that the basis will not be a regular triangle with equal legs.
Add 8-10 mm to the resulting opening width, depending on the thickness of the sidewalls. This is necessary so that the facade is covered by the end and it does not “look through” against the general background of the single façade part.
Advice! Do not try to calculate the dimensions of the radius front for a cabinet with a concave or convex shape. As a rule, this is useless - most manufacturers limit themselves to producing standard shapes of certain sizes. Here they act from the “opposite”: they find out the dimensions of the door and design a cabinet for it (or use ready-made diagrams, usually developed by the manufacturers themselves). And the remaining modules are “adjusted” to the resulting corner.
Standard sizes of kitchen cabinet fronts
It is always cheaper to buy facades of standard sizes than to order non-standard ones. It's also faster: custom ones will have to wait for them to be made, while standard ones can be purchased in stock. Therefore, when designing a kitchen, we start from a table of standard sizes of facades. The result will be significant savings. With the right approach, non-standard facades will only be needed for end modules. Which, however, can be made in the form of open shelves.
The layout of standard sizes of facades on kitchen cabinets can be more clearly represented in the drawing.
It is also recommended to take a tabular form from the manufacturer in advance - for example, Ikea’s standards differ significantly from the generally accepted ones. And already design the kitchen based on what you have.
By the way, kitchen facades can be equipped with almost any furniture in the house: good options can be selected for making children’s rooms, wall slides in the living room and other low cabinet furniture.
Source
Types of kitchen fronts
Before purchasing furniture for your home, you need to decide on the type of facades that will be used. Today, manufacturers offer two types of fronts - standard and non-standard. Each of them has its own advantages, so it doesn’t hurt to understand how these categories differ.
Facades made according to individual calculations are a more flexible solution for renovation. They allow you to realize the customer’s own ideas, use the space in the room more intelligently, and also fit better with non-standard-shaped furniture. However, you should be aware that the cost of such work may be a third more expensive, and the production time will increase by several days.
Standard facades are quite suitable in most cases when there is no need to make any special design for the room. They are cheaper, easier to design, and easy to add components and other parts to. Modern furniture companies try to take into account the needs of users, so they produce products for various types of premises - with different arrangements of walls and ceilings, the presence of niches and recesses, large or small dimensions. Therefore, for a kitchen with a conventional layout, it is enough to simply purchase ready-made factory facades.